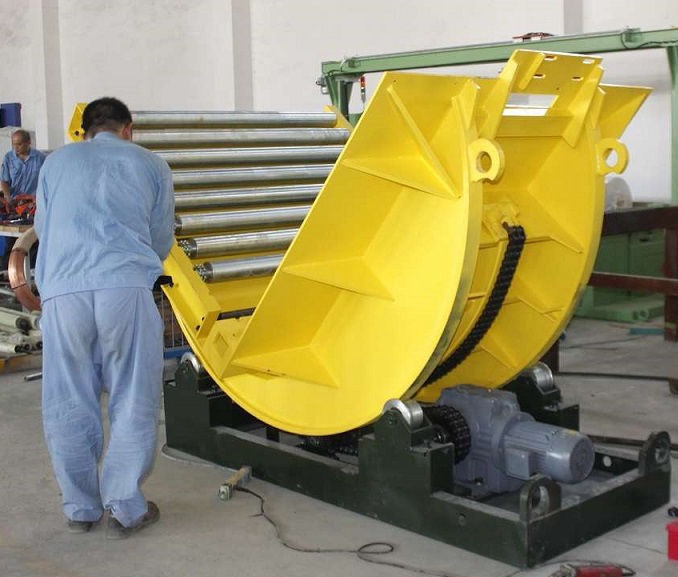
Coil Upender Machines for Safe Coil Lifting and Positioning in Logistics?
Every day in metal processing facilities, workers face the dangerous task of moving heavy coils. Manual handling causes slow operations and serious safety risks. Plant managers like Michael Chen struggle with these challenges daily, watching productivity drop and injury risks rise. The constant threat of equipment failure and worker accidents keeps them searching for reliable solutions.
Coil upender machines are specialized material handling equipment that safely rotate, lift, and position heavy coils in logistics and manufacturing operations, eliminating manual handling risks while improving workflow efficiency. These hydraulic or electric-powered systems provide controlled coil rotation from horizontal to vertical orientations, ensuring precise positioning for downstream processes while maintaining workplace safety standards. Proper coil orientation equipment reduces product damage and operator injury risks significantly.
Understanding how coil upender technology transforms material handling requires examining specific operational benefits, technical specifications, and implementation strategies that address common industrial challenges faced by logistics professionals and plant managers.
1. What Safety Features Make Coil Upenders Essential for Modern Logistics Facilities?
Workplace accidents involving heavy coil handling continue to plague metal processing industries. Manual coil turning operations expose workers to crushing hazards, muscle strains, and falling load risks. Insurance claims and production delays from these incidents cost companies thousands annually, creating urgent need for engineered safety solutions.
Coil upenders incorporate multiple safety systems including emergency stop buttons, hydraulic safety valves, mechanical locking devices, and overload protection to prevent accidents during coil rotation and positioning operations. These integrated safety mechanisms ensure controlled movement throughout the lifting cycle, with backup systems activating automatically if primary systems fail. Advanced models include infrared presence detection that halts operation when workers enter danger zones.
🛡️ Critical Safety Components in Modern Coil Upenders
| Safety Feature | Protection Type | Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|
| Dual-hand operation | Operational control | Prevents accidental activation |
| Emergency stop circuits | Immediate shutdown | Responds to unexpected situations |
| Hydraulic safety valves | Pressure control | Prevents overload conditions |
| Mechanical locks | Position security | Secures coils during rotation |
| Load sensors | Weight monitoring | Detects capacity exceedance |
| Safety fences | Physical barriers | Creates operator exclusion zones |
Emergency stop systems provide instant machine shutdown capability from multiple locations around the equipment. These red mushroom-head buttons are strategically positioned for quick access during emergencies. Hydraulic safety valves automatically regulate system pressure, preventing excessive force that could damage coils or equipment structure.
Load monitoring technology represents another crucial safety advancement. Modern upenders include weight sensors that detect when loads approach or exceed rated capacity. These systems trigger visual and audible warnings, then automatically prevent operation if dangerous conditions exist. This technology prevents structural overloading that could lead to catastrophic equipment failure.
Physical guarding solutions complement electronic safety systems. Fixed and interlocked guards create barriers between workers and moving components. Interlocked systems automatically disable machine operation when guards are opened, ensuring no access to pinch points during cycle times. These layered protection approaches have reduced coil handling injuries by up to 72% in facilities that implemented proper upender systems.
(industrial coil handling safety standards, material handling equipment protection features, warehouse injury prevention technology)
2. How Do Coil Upender Machines Improve Operational Efficiency in Steel Logistics?
Traditional coil handling methods create significant bottlenecks in metal processing workflows. Manual coil rotation requires multiple workers, consumes valuable time, and introduces inconsistent positioning that slows downstream operations. These inefficiencies ripple through entire production lines, delaying shipments and increasing labor costs.
Coil upender machines dramatically improve operational efficiency by reducing coil positioning time from 15-20 minutes manually to under 2 minutes automatically, while enabling single-operator functionality instead of requiring 2-3 person teams. This efficiency gain translates to approximately 78% reduction in labor requirements for coil handling tasks, with additional time savings from eliminated repositioning needs and consistent orientation accuracy.

Efficiency Metrics Comparison: Manual vs. Automated Coil Handling
- Labor Requirements: Manual handling (3 workers) → Upender system (1 operator)
- Positioning Time: Manual method (18 minutes average) → Upender (90 seconds)
- Repositioning Needs: Manual (frequent adjustments) → Upender (single operation precision)
- Shift Capacity: Manual (15-20 coils) → Upender (40-50 coils)
- Fatigue Impact: Manual (significant productivity decline) → Upender (consistent performance)
Process integration capabilities further enhance efficiency gains. Modern upenders interface seamlessly with conveyor systems, coil cars, and processing equipment. This integration creates continuous material flow without intermediate handling stages. For example, coils can transfer directly from upender discharge to packaging stations or storage systems, eliminating double-handling.
The consistency of automated positioning provides perhaps the most valuable efficiency benefit. Unlike manual methods that produce variable results, upenders deliver identical coil orientation every cycle. This predictability allows downstream equipment operators to work at optimal speeds without adjustment delays. Production planning becomes more accurate when coil positioning time becomes a fixed variable rather than an unpredictable manual operation.
Equipment reliability directly impacts overall efficiency. High-quality upenders from manufacturers like Fengding and Wuxi Buhui maintain 95%+ uptime with proper maintenance. This reliability eliminates the production disruptions common with less robust equipment. The return on investment typically ranges from 8-15 months based on reduced labor costs, increased throughput, and lower product damage rates.
(automated coil positioning systems, steel logistics efficiency improvements, material handling productivity metrics)
3. What Technical Specifications Should You Consider When Selecting Coil Upender Equipment?
Choosing inappropriate coil upender specifications leads to operational limitations, safety compromises, and premature equipment failure. Many facilities make the mistake of selecting undersized machines or overlooking critical features that address their specific application requirements, resulting in continuous operational challenges.
Key technical specifications for coil upender selection include load capacity (3-30+ tons), rotation angle (90°-180°), power system (hydraulic/electric), control type (manual/automated), and physical dimensions that fit your facility layout and workflow requirements. Understanding these parameters ensures the selected equipment matches both current needs and future production expansion plans.
📊 Coil Upender Specification Checklist
Capacity Requirements
- Maximum coil weight: __ tons
- Coil diameter range: __ - __ mm
- Coil width range: __ - __ mm
- Future capacity needs: __ tons
Rotation Specifications
- Required rotation angle: 90° / 180° / __°
- Rotation speed: __ RPM
- Positioning accuracy: ± __ mm
Power & Control Systems
- Hydraulic pressure: __ psi
- Motor power: __ kW
- Control interface: Manual / Semi-auto / Full-auto
- Safety system redundancy: Single / Dual
Load capacity represents the most fundamental specification. Beyond simply matching maximum expected coil weight, consider capacity headroom for unexpected heavy coils and future production requirements. Leading manufacturers like Fengding recommend 15-20% capacity margin beyond current maximum needs. This buffer accommodates weight variations and protects against premature wear.
Rotation mechanism design significantly impacts performance and maintenance needs. Hydraulic systems dominate heavy-duty applications (5+ tons) for their power and smooth operation. Electric drive systems suit lighter applications where precision positioning takes priority over raw power. The rotation bearing design determines longevity—roller bearings withstand heavy loads better than bushing-type designs.
Control system sophistication should match operational requirements. Basic manual controls suffice for low-volume applications, while programmable systems benefit high-volume operations. Advanced controls enable integration with factory management systems, providing operational data and performance analytics. These systems track cycle counts, maintenance intervals, and efficiency metrics automatically.
Physical dimensions and facility integration requirements deserve careful attention. Measure available space including ceiling height, door access, and foundation requirements. Consider workflow connections to adjacent equipment—proper interface dimensions prevent material handling bottlenecks. Customizable upenders from specialized manufacturers often provide better long-term value than standardized models with compromised fit.
(coil upender technical specifications, material handling equipment selection criteria, industrial machinery capacity planning)
4. How Can Proper Coil Upender Implementation Solve Common Metal Processing Challenges?
Metal processing facilities face consistent operational challenges that extend beyond basic coil handling needs. Product damage during orientation, space constraints, integration difficulties with existing equipment, and training requirements often undermine the potential benefits of upender implementation without proper planning and execution.
Strategic coil upender implementation addresses multiple metal processing challenges simultaneously by reducing product damage rates by up to 45%, decreasing required floor space through vertical integration, enabling seamless equipment connectivity, and incorporating intuitive operation that minimizes training time. This comprehensive approach transforms upenders from standalone equipment into integrated productivity solutions.

Problem-Solution Framework for Coil Upender Implementation
| Common Challenge | Implementation Solution | Outcome Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Product damage | Cradle design with protective lining | 45% reduction in edge damage |
| Space limitations | Compact footprint with vertical operation | 30% less floor space vs manual |
| Equipment isolation | Interface standardization | 85% faster material transfer |
| Skill dependency | Simplified control systems | 50% shorter training time |
| Maintenance complexity | Modular component design | 60% faster repair turnaround |
Product damage prevention begins with proper cradle design. Customizable contact surfaces with replaceable wear plates and non-marking materials protect coil surfaces during rotation. Pressure distribution systems ensure even support across the coil width, preventing edge distortion that occurs with improper support methods. These features become particularly valuable when handling pre-finished materials where surface preservation is critical.
Space optimization strategies make upenders viable even in constrained facilities. Rotational operation inherently requires less clearance than linear transfer systems. Compact models from manufacturers like Wuxi Buhui fit into existing production gaps without major facility modifications. Vertical integration—stacking functions within the same footprint—further maximizes space utilization. For example, combining upending with weighing or inspection operations in one station.
Integration methodology determines overall system effectiveness. Proper interface planning ensures smooth material transfer between upenders and adjacent equipment. Standardized height matching, conveyor synchronization, and control system compatibility eliminate transfer bottlenecks. Implementation should include mock-up testing of material flow using actual coil dimensions before final equipment installation.
Operator training and acceptance directly impact implementation success. Intuitive control systems with clear visual indicators reduce learning curves. Progressive disclosure of functions—basic operations first, advanced features later—prevents overwhelm. Involvement of experienced operators during equipment selection improves buy-in and identifies potential operational friction points early. Proper implementation turns equipment into solutions.
(metal processing challenges solutions, coil upender implementation strategies, industrial equipment integration methods)
Conclusion
Coil upender machines transform coil handling operations by combining safety, efficiency, and precision in heavy-duty industrial applications. Implementing the right upender system creates safer workplaces while optimizing your complete steel coil packing line for maximum productivity and reliability.
